What is Resonance - Types and Applications
What is Resonance- Types and Applications
Definition: “When a periodic force is applied on a
vibrating body such that the frequency of the applied force becomes equal to
the natural frequency of oscillating or vibrating body, then there is an
increase in the amplitude of the vibrating body. These phenomenon is called as
resonance”.
i.
Under
resonance condition, the energy supplied by the driving force is just
sufficient to overcome friction in the system.ii. Resonance occurs when the frequency of the applied periodic force is an integral multiple of the natural frequency of a body, then the resonance take place at;
Resonant Frequency
A resonant frequency is the natural
vibrating frequency of an object and is usually denoted as f with a subscript
zero (f0).
Resonance is witnessed in objects
that is in equilibrium with acting forces and could keep vibrating for a long
time under perfect conditions.
To find the resonant frequency of a
single continuous wave, we use the formula
v = fλ f = v/λ
Where,
v is the wave velocity
λ is the distance of the wavelength
Types of Resonance
There are many types of resonance,
and they are:
Mechanical Resonance
Mechanical resonance can be defined
as the tendency of a mechanical system to respond at greater amplitude when the
frequency of its oscillations matches the system’s natural frequency of
vibration (its resonance frequency or resonant frequency) than it does at other
frequencies. The resonant frequency of a spring is calculated using the given
formula:
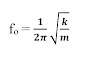
Electrical
Resonance
In a circuit when the inductive
reactance and the capacitive reactance are equal in magnitude electrical
resonance occurs. The resonant frequency in an LC circuit (Inductive-Capacitive circuit) is given by the
formula:
Acoustic Resonance
Acoustic resonance is a phenomenon
in which an acoustic system amplifies sound waves whose frequency matches one
of its own natural frequencies of vibration. Acoustic resonance is an important
consideration for instrument builders as most acoustic instruments such as the
length of tube in a flute, the strings and body of a violin and the shape of a
drum membrane use resonators. Acoustic resonance is also important for hearing.
Applications of Resonance:
i. It is used to find the natural frequency of the different bodies.ii. It is used to determine the speed of sound with resonance tube apparatus.
iii. Resonance can be used to determine the frequency of a given body.
iv. Mechanical and electrical systems shows a good response under phenomenon of resonance.
v. Magnetic resonance imaging has greatly improved medical diagnosis.
vi. Cooking of foods in microwave oven is due to resonance.
vii. Radio receiver works on the principle of resonance.




Post a Comment
2 Comments
Good blog
ReplyDeleteWell explained
ReplyDeleteYour Comments are highly appreciated